This article will explain to you how to build a nodejs application with Docker containerization. Docker allows to package and run applications as containers.
Today we are starting a series of tutorials about software development tools. And this first article covers how to containerize a Node.js application using Docker. Docker helps developers to package and run applications as containers. Since the container is an isolated process and a lightweight alternative to virtual machines. This article explains how to build a nodejs application with Docker containerization. Let’s get started!
- What is Docker
- Prerequisites
- Setup Node.js Application
- Write Dockerfile
- Build Image and Run Docker Container
- Conclusion
What is Docker
Docker is a set of platform as a service products that use OS-level virtualization to deliver software in packages called containers. It is an open platform for developing, shipping, and running applications. Docker enables you to separate your applications from your infrastructure so you can deliver software quickly.
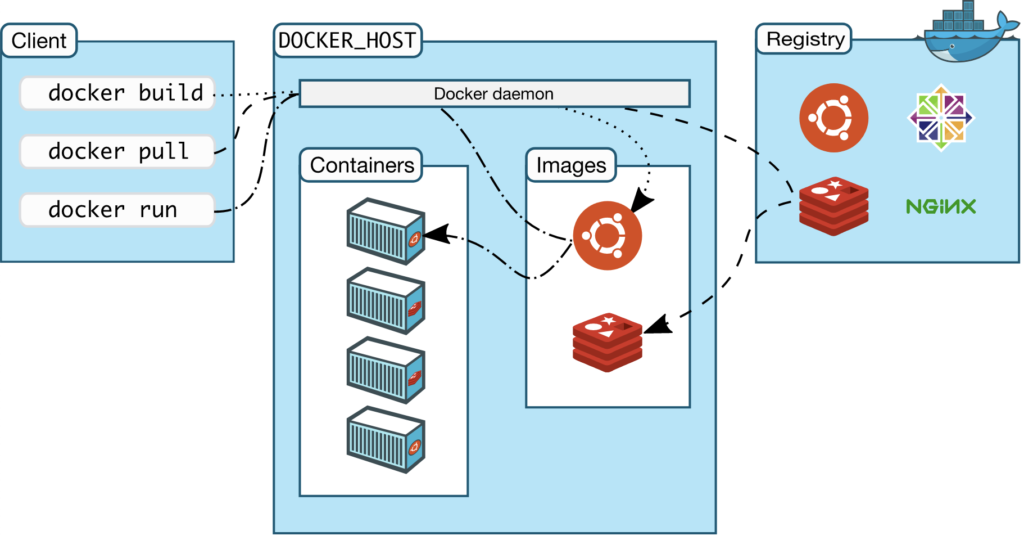
Docker uses a client-server architecture. The Docker client talks to the Docker daemon, which does the heavy lifting of building, running, and distributing your Docker containers. The Docker client and daemon communicate using a REST API, over UNIX sockets or a network interface. Here is the diagram of docker architecture.
Prerequisites
- Ubuntu Server
- Docker Installed on the Server
- Node.js npm installed
Setup Node.js Application
To create your image, you will first need to make your application files, which you can then copy to your container. These files will include your application’s static content, code, and dependencies.
First, create a directory for your project in your non-root user’s home directory. Then, execute below command in a new folder that you created.
npm init -y
npm i -s express
The above command will set up a Node.js application with express framework installed as a dependency. Let’s add the following code into app.js file.
const express = require(‘express’);
const app = express();
app.get(‘/’, function(req,res){
res.send(“Hello World”);
});
const port = 3000;
app.listen(port, function () {
console.log(‘Listening on port 3000!’)
})
Start the application with node app.js
node app.js
Navigate your browser to http://your_server_ip:3000. You will see the following landing page.
Now you have an application up and running. We can now move on to create the Dockerfile that will allow us to recreate and scale this application.
Write Dockerfile
Using Dockerfile, you can specify what will be included in your application container when it is executed and the container environment.
First of all create Dockerfile with following command at the root of your project.
vi Dockerfile
Add the following FROM instruction to set the application’s base image:
FROM node:12-alpine
You can add .dockerignore file in order to remove files that not belongs to docker image.
Let’s create the node_modules subdirectory in /home/node along with the app directory. This will ensure that they have the needed permissions, which will be important when we create local node modules in the container with npm install.
...
RUN mkdir -p /home/node/app/node_modules && chown -R node:node /home/node/app
Next, set the working directory of the application to /home/node/app:
...
WORKDIR /home/node/app
Next, copy the package.json and package-lock.json, assign the project file to a non-root user “node” and then run the npm install
...
COPY package*.json ./
USER node
RUN npm install
Copy your application code with the appropriate permissions to the application directory on the container
...
COPY --chown=node:node . .
EXPOSE command to expose port:
...
EXPOSE 3000
CMD [ "node", "app.js" ]
Final version of Dockerfile should look like this:
FROM node:12-alpine
RUN mkdir -p /home/node/app/node_modules && chown -R node:node /home/node/app
WORKDIR /home/node/app
COPY package*.json ./
USER node
RUN npm install
COPY --chown=node:node . .
EXPOSE 3000
CMD [ "node", "app.js" ]
Build Image and Run Container
Run the following command to generate your Docker Image
docker build -t <<image_name>> .
This will generate a docker image which you can check by using the docker images command. It is now possible to create a container with this image using the following command:
docker run — name <<container_name>> -p 3000:3000 -d <<image_name>>
This will start the container which you can verify by running the docker ps command. Now in your browser if you access http://localhost:3000 you’ll see your Node.js app running. However this time now its running from your Docker container.
Conclusion
Development with the Docker Container is is very simple and easy. Docker helps developers to package and run applications as containers. In this tutorial we learned how to build a node.js application using docker container on Ubuntu. In upcoming articles we’ll write about more uses of Docker and also we’ll discuss other tools.